BIM implementation at Architecture/Interior design Firms
BIM implementation refers to the process of adopting and utilizing BIM within a construction project or an organization. This involves using BIM models for design analysis, visualization, clash detection, quantity takeoffs, scheduling, and other project-related activities to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Successful BIM implementation requires a combination of technical expertise, organizational commitment, and effective communication among project stakeholders.
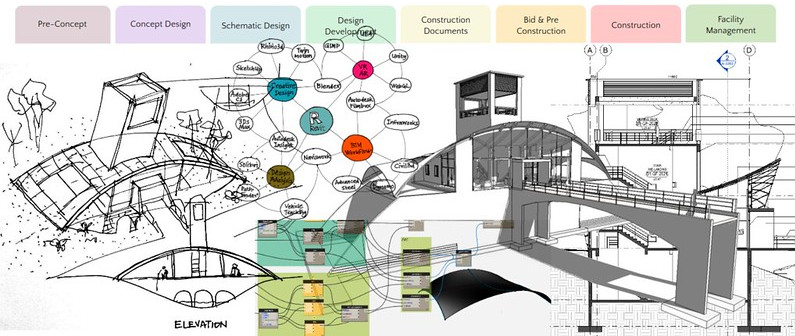
Design and BIM Workflow
Define the goals
Clearly define the objectives and goals of implementing BIM. Determine what you aim to achieve through BIM adoption, such as improving collaboration, reducing errors and rework, enhancing project visualization, or optimizing facility management.
Plan and strategize
Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that outlines the steps, timeline, and resources required for successful BIM adoption. Consider factors such as budget, training needs, technology infrastructure, and project-specific requirements.
Allocate resources
Ensure you have the necessary resources, both in terms of personnel and technology, to support BIM implementation. This includes acquiring the appropriate software tools, hardware, and IT infrastructure to enable efficient BIM workflows.
Train and educate staff
Provide training and education to employees involved in the BIM process. This includes not only technical training on BIM software but also educating stakeholders about the benefits of BIM and how it affects their roles and responsibilities.
Establish BIM standards and protocols
Develop and implement standardized processes and protocols for BIM usage across projects and teams. This includes defining file naming conventions, modeling guidelines, data exchange formats, and coordination procedures to ensure consistency and interoperability.
Collaborate and coordinate
Foster a collaborative environment where all project stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and subcontractors, actively participate in the BIM process. Encourage regular coordination meetings and information sharing to leverage the full potential of BIM for improved project outcomes.
Integrate BIM into workflows
Incorporate BIM processes and deliverables into project workflows. This involves using BIM models for design analysis, clash detection, quantity takeoffs, scheduling, and other project-related activities to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Data management and maintenance
Establish data management practices to ensure the integrity, security, and longevity of BIM data throughout the project lifecycle. Implement backup and version control systems to manage model iterations and revisions effectively.
Evaluate and refine
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of BIM implementation and gather feedback from project teams. Identify areas for improvement and refine the BIM workflows and processes accordingly.
Stay updated
Keep up with advancements in BIM technology, industry standards, and best practices. Attend conferences, join industry groups, and stay connected with the BIM community to stay informed about emerging trends and innovations.
Summary
Overall, BIM offers numerous benefits throughout the entire lifecycle of a building or infrastructure project, including improved collaboration, enhanced visualization, clash detection, cost and time management, facility management, and sustainability analysis. These advantages lead to better project outcomes, reduced costs, increased efficiency, and improved decision-making in the AEC industry.
Successful implementation of BIM provides the design firm better results and competitive advantage in its market segment.